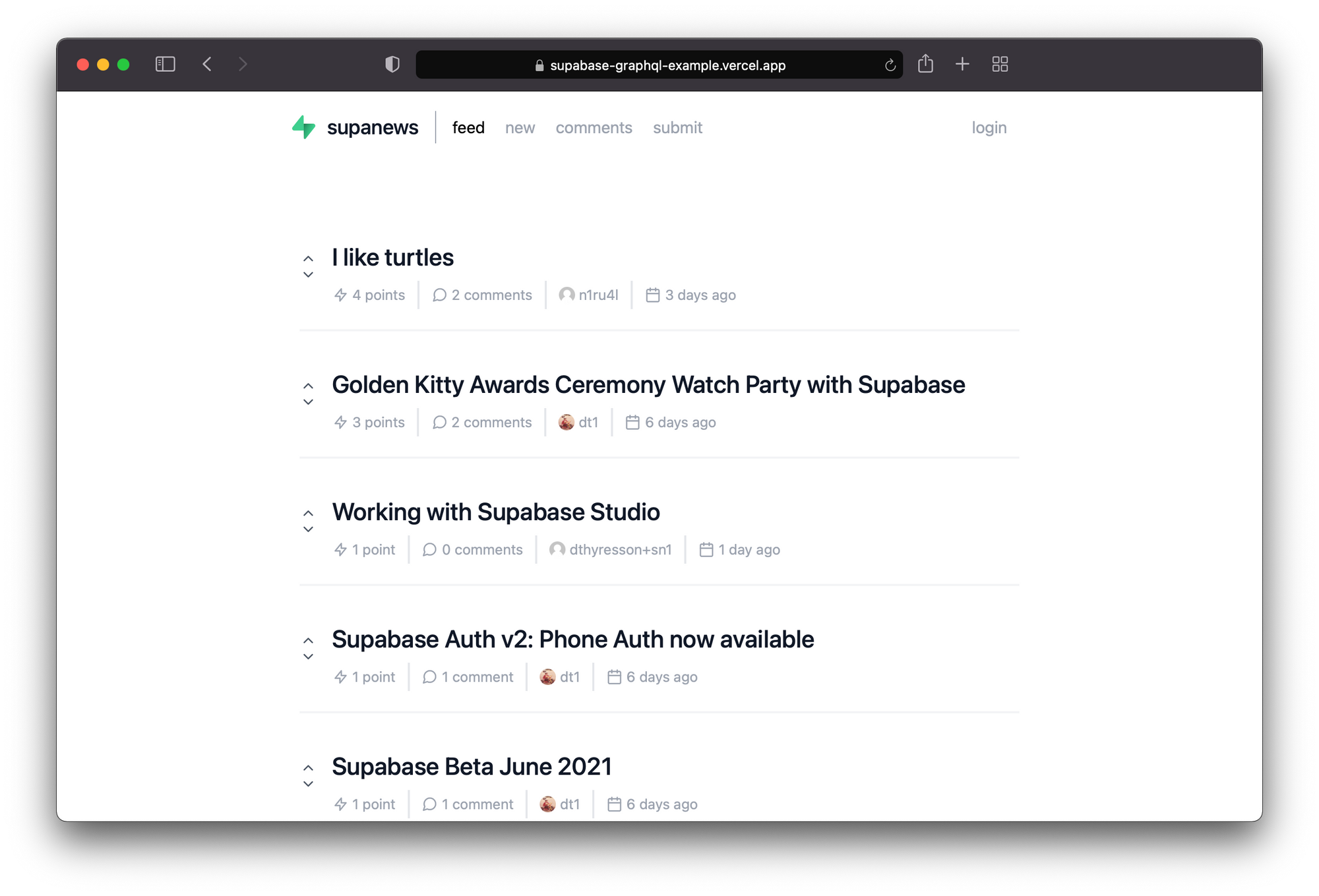
A start/home page for your favorite websites.
- Free and open-source.
- Local and offline.
- No hidden scripts.
- Shortcut for your favorite websites, meaning your favorite and most used websites in one page.
- Native/Pure JavaScript.
- Files to edit/manage your favorite websites.
- One file to add a new website.
- Easy to customize.
- Dark & Light mode.
- Multiple search engines.
- Multiple custom versions.
https://m-primo.github.io/psbp/index.html
NOT UP-TO-DATE
https://chrome.google.com/webstore/detail/your-browsing-homepage/gankljibcichebamdgagnnncmnoacdmi
NOT UP-TO-DATE
https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/your-browsing-homepage/
Open userSites.js, then add a code like the syntax bellow:
new Site("Website Name", "full url with http or https", "iconname.ext", "Description (you can leave it empty)");
For example, if you want to add Blogger:
new Site("Blogger", "https://blogger.com", "b.png");
DO NOT FORGET TO ADD THE IMAGE IN THIS DIRECTORY: img/site.
To add an external icon, just add true at the end:
For example:
new Site("Website Name", "full url with http or https", "http://www.example.com/iconname.ext", "Description (you can leave it empty)", true);
Just replace http://www.example.com/iconname.ext with the actual image url.
First: Create your userSites script file, and the name should be like this: version_userSites.js.
For example, if you want to name your version personal, so the script file name should be: personal_userSites.js.
Second: Add the websites you want in that newly created file, just like in userSites.js.
Finally: To access the homepage with your created version, you should add ?version=version in the URL bar.
For the above example, you should add ?version=personal in the URL bar, and it’ll load your websites you added in personal_userSites.js file. In other words, if your version is personal and the current homepage link is https://example.com, you can access it like this: https://example.com?version=personal.
Pull requests are welcome. For major changes, please open an issue first to discuss what you would like to change.