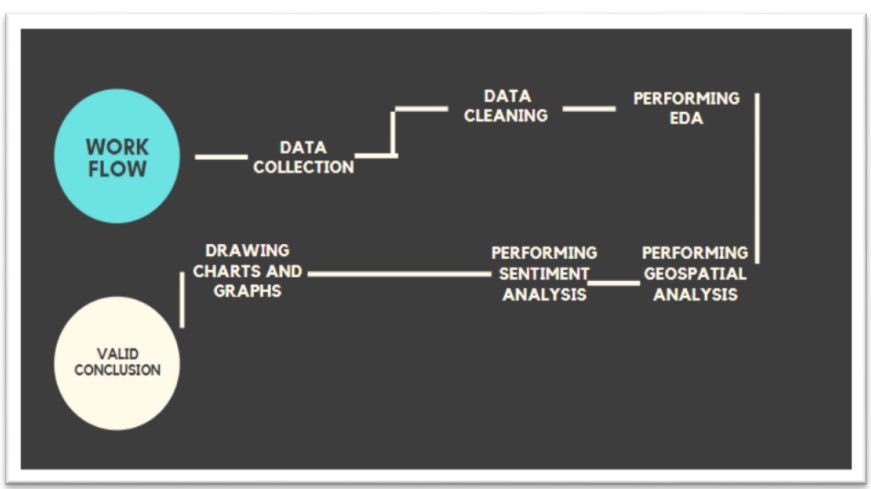
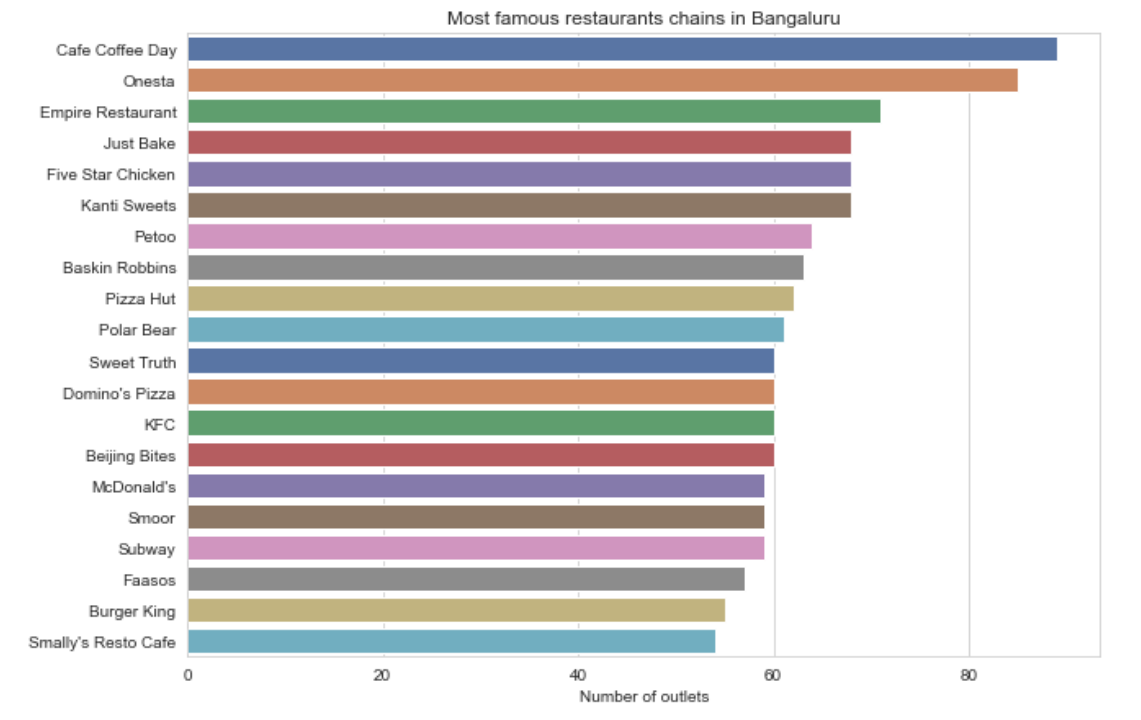
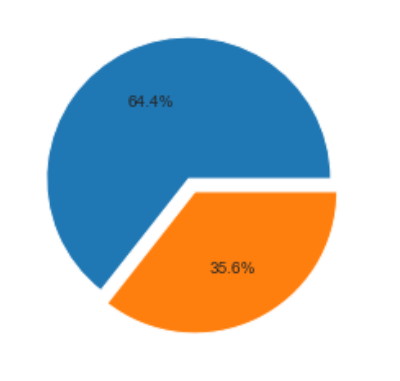
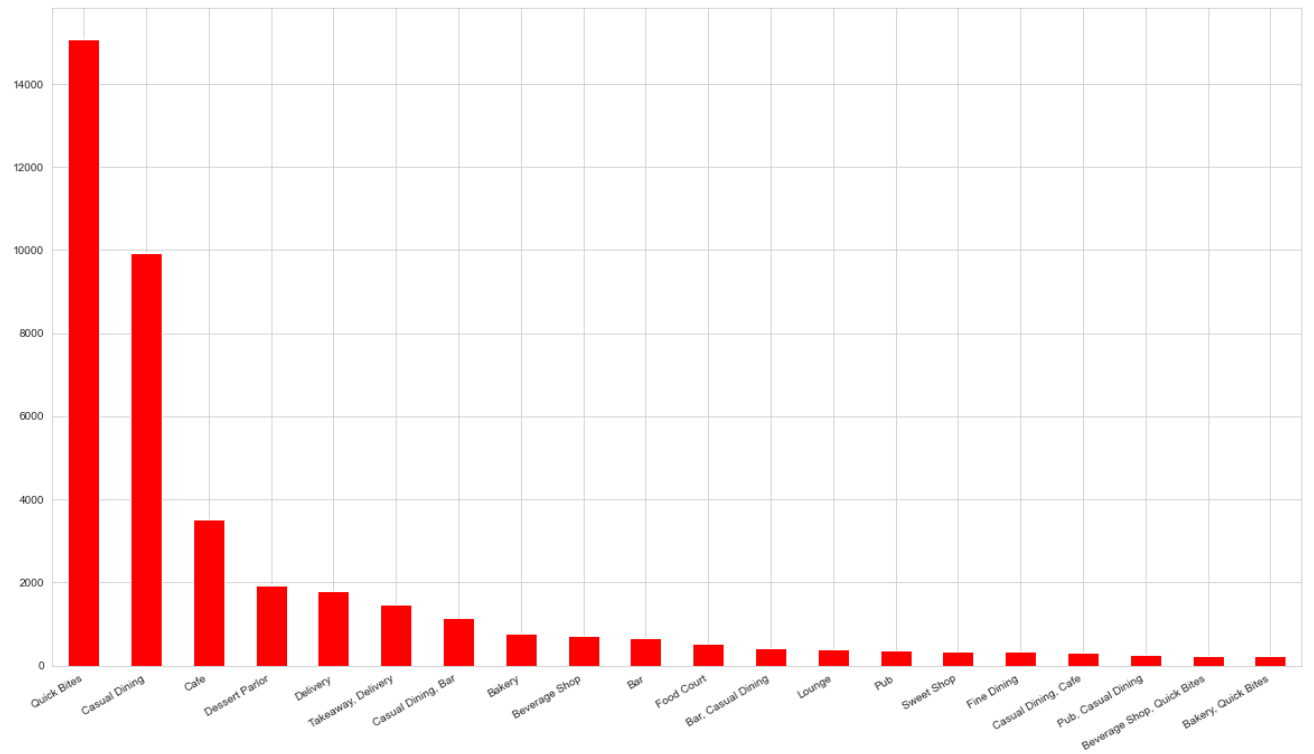
Common web and node.js grunt tasks/lint configs/md templates and so on…
This library holds common build tasks, lint configuration and so on, used by my personal node.js and web projects.
This allows for a central configuration for all projects.
In order to use this library, you need to refactor your build processes as defined in some of my projects such as simple-oracledb
In order to use this library, just run the following npm install command:
npm install --save-dev js-project-commonsSee full docs at: API Docs
| Date | Version | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 2021-02-08 | v1.3.2 | Upgrading dependencies |
| 2020-05-11 | v1.3.1 | Support web projects without bower.json |
| 2020-05-11 | v1.3.0 | Update CI and ES6 syntax |
| 2019-10-07 | v1.2.1 | Update eslint rules |
| 2018-06-14 | v1.1.11 | Common karma config |
| 2018-06-13 | v1.1.6 | Karma browser to be defined in karma conf and not in grunt task |
| 2018-04-30 | v1.1.3 | node 10 support |
| 2018-04-23 | v1.1.1 | Update htmllint options |
| 2018-04-14 | v1.1.0 | Add support of node >=6 grunt tasks |
| 2018-01-17 | v1.0.99 | Remove lock files automatically |
| 2017-11-06 | v1.0.98 | Update mocha options |
| 2017-07-19 | v1.0.96 | Disable jslint by default |
| 2017-05-01 | v1.0.89 | Load env vars from file for build process |
| 2017-04-28 | v1.0.83 | Add support for simple dual web/node projects |
| 2017-04-24 | v1.0.76 | Added snyk validations |
| 2017-04-17 | v1.0.72 | Added YAML validations |
| 2017-04-11 | v1.0.68 | Modify stylelint rules configuration |
| 2017-02-13 | v1.0.63 | jsdoc2md fix for windows |
| 2017-02-11 | v1.0.62 | Added env validation for build |
| 2017-01-13 | v1.0.60 | No security validation for npm dependencies for web projects |
| 2017-01-13 | v1.0.59 | Adding file name linting |
| 2017-01-06 | v1.0.57 | Updated api docs to readme generation task |
| 2016-12-21 | v1.0.54 | Adding htmlhint to grunt build |
| 2016-12-16 | v1.0.50 | Adding stylelint to grunt build |
| 2016-12-15 | v1.0.48 | Adding security validations to grunt build |
| 2016-11-26 | v1.0.44 | Create github release grunt task |
| 2016-11-19 | v1.0.34 | Build dependencies are now packaged and loaded internally |
| 2016-09-21 | v1.0.18 | Added api docs to readme generation task |
| 2016-09-15 | v1.0.17 | jslint will test spec files |
| 2016-09-14 | v1.0.15 | jshint and jscs will test also spec files |
| 2016-09-13 | v1.0.13 | Adding html and css linting support |
| 2016-09-12 | v1.0.10 | eslint will test also spec files |
| 2016-09-10 | v1.0.3 | Grunt tasks are now grouped to node/web build configs |
| 2016-09-07 | v1.0.1 | Lazy loading of grunt task definitions |
| 2016-09-07 | v1.0.0 | Change hosted lint configurations |
| 2016-09-07 | v0.0.2 | Initial release. |
Developed by Sagie Gur-Ari and licensed under the Apache 2 open source license.
 https://github.com/sagiegurari/js-project-commons
https://github.com/sagiegurari/js-project-commons