An introduction to Symfony 4.
Requirements: Composer & MySQL service running.
# Install dependencies
composer install
# Create and edit the ".env.local" file and add DB params
# Run in development mode
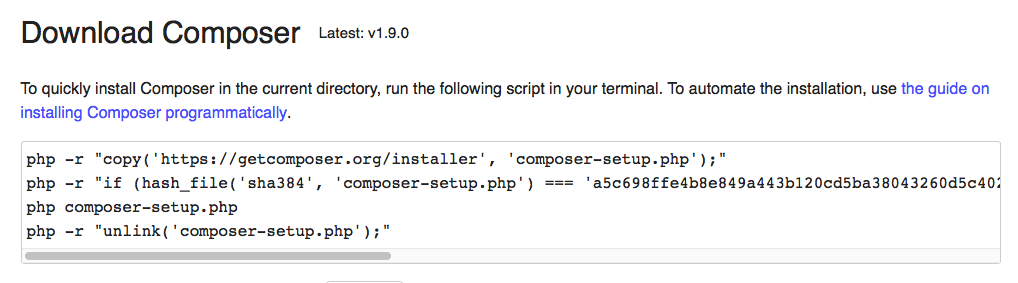
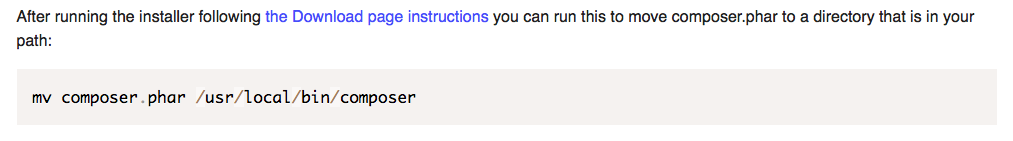
php bin/console server:runInstall Composer (globally)

 Check with command:
Check with command: composer -V.
Then navigate to directory “/Applications/XAMPP/xamppfiles/htdocs/sites” (or your public web server directory) and create a new Symfony proyect with this command: composer create-project symfony/skeleton symphart.
NOTE: I created this project inside a folder called “sites” but you can skip that folder if you prefer create a virtual host. Another option is use “Symfony PHP web server” as described after.
Start your web server (Apache) and load in your browser this URL: http://localhost/sites/symphart/public/
TIP: You can create a basic
.htaccessfile inside “/public” folder.
Install “Symfony PHP web server” using command: composer require symfony/web-server-bundle --dev.
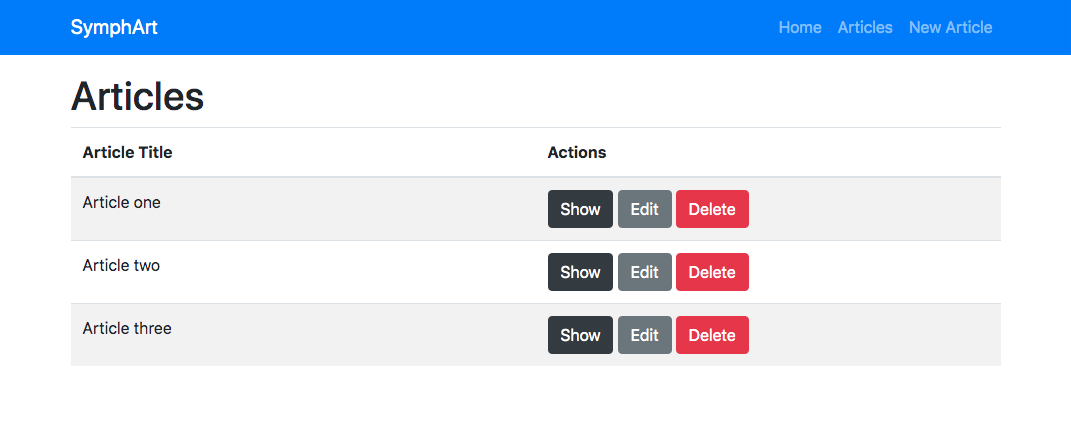
Creater your first controller:
// src/Controller/ExampleController.php
<?php
namespace App\Controller;
use Symfony\Component\HttpFoundation\Response;
class ExampleController {
public function index() {
return new Response('<html><body><h1>It's just an example</h1></body></html>');
}
}
And define your first route:
// config/routes.yaml
index:
path: /
controller: App\Controller\ExampleController::index
For start server in development mode: php bin/console server:run. Observe how a web server start serving your applicattion on localhost on an specific port.
Et Voilà! You are ready to work.
- Install Annotations to define routes inside controllers:
composer require annotations - Install Twig as template engine:
composer require twig - Install Doctrine:
composer require doctrine maker.- If you want to use a database, you must create a copy of file
.envand rename as.env.localand then define your SQL credentials and database name. - Then execute
php bin/console doctrine:database:create. - Now you can create entities with the command
php bin/console make:entity Foo(where “Foo” will be the name of entity). You can use the same command to update an existing entity - Execute
php bin/console doctrine:migrations:diffto create migration file. Database migrations are a way to safely update your database schema both locally and on production. Then execute the migration with the commandphp bin/console doctrine:migrations:migrate. Now your database will be upgrade to new structure. - If you edit Entity files, you need to run
php bin/console doctrine:migrations:diffandphp bin/console doctrine:migrations:migratecommands to sync database.
- If you want to use a database, you must create a copy of file
- Install Assets manager:
composer require symfony/asset - Install form component:
composer require form
- Examinate your routes:
php bin/console debug:router - Execute queries to database from console:
php bin/console doctrine:query:sql 'SELECT * from article'
- This repository contains the exercise explained in this YouTube Tutorial
- Symfony docs
- Composer docs

Leave a Reply